Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal disorder, but its diagnosis can be challenging due to the absence of specific tests or visible structural abnormalities. In this blog, we will unravel the journey to diagnosing IBS, shedding light on the key steps involved in this process.
The Diagnostic Criteria
The diagnosis of IBS relies on a set of clinical criteria known as the Rome IV criteria. These criteria help healthcare providers identify individuals who are likely to have IBS based on their symptoms. To meet the criteria for an IBS diagnosis, a person must experience recurrent abdominal pain or discomfort for at least three days a month for the past three months. This discomfort or pain should be associated with two or more of the following:
- Improvement with Defecation: Pain is alleviated after a bowel movement.
- Onset Associated with a Change in Frequency of Stool: Symptoms coincide with changes in bowel habits (diarrhea, constipation, or both).
- Onset Associated with a Change in Form (Appearance) of Stool: Symptoms coincide with changes in stool consistency.
A- Medical History and Symptom Evaluation
The diagnosis journey begins with a comprehensive medical history and symptom evaluation. Your healthcare provider will ask detailed questions about your symptoms, including:
- The nature of abdominal pain or discomfort.
- The duration and frequency of symptoms.
- Any triggers or exacerbating factors, such as specific foods or stress.
- The presence of other symptoms, such as bloating, gas, or mucus in the stool.
B- Rule Out Other Conditions
IBS is a diagnosis of exclusion, meaning that other gastrointestinal conditions must be ruled out before confirming IBS. Common conditions that mimic IBS symptoms include:
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis can present with abdominal pain and changes in bowel habits.
- Celiac Disease: Gluten sensitivity can cause gastrointestinal symptoms similar to IBS.
- Colon Cancer: In some cases, colon cancer may manifest with IBS-like symptoms, particularly in older adults.
C- Diagnostic Tests
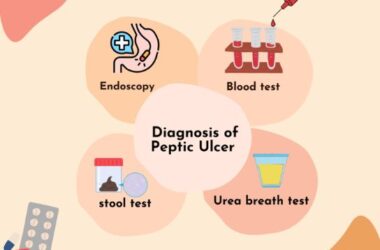
To rule out other conditions and ensure the accuracy of the diagnosis, your healthcare provider may recommend various diagnostic tests:
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can help detect signs of inflammation, infection, or anemia, which can provide clues about underlying conditions.
- Stool Tests: Stool tests may be conducted to rule out infections, parasites, or other gastrointestinal issues.
- Colonoscopy or Endoscopy: In some cases, your healthcare provider may recommend these procedures to visualize the gastrointestinal tract and obtain biopsies to rule out IBD or other structural abnormalities.
Treatment and management of IBS
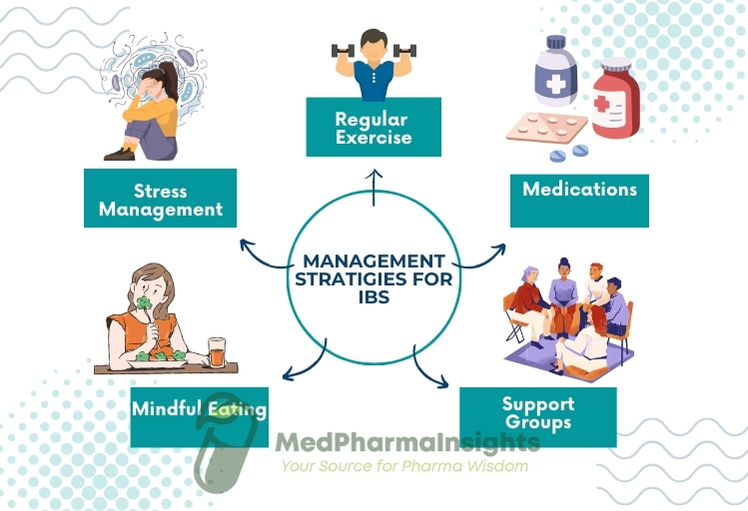
There are various strategies for the treatment and management of IBS, empowering individuals to lead more comfortable lives.

1. Dietary Modifications
- Low-FODMAP Diet: Some individuals with IBS find relief by following a low-FODMAP diet, which restricts certain types of fermentable carbohydrates that can trigger symptoms. A registered dietitian can help guide you through this dietary approach.
- Fiber: For those with constipation-predominant IBS (IBS-C), increasing dietary fiber intake or taking fiber supplements may help regulate bowel movements. Soluble fiber sources like oats, psyllium, and flaxseeds are often recommended.
- Avoid Trigger Foods: Identify and avoid specific foods that exacerbate your symptoms. Common triggers include high-fat foods, caffeine, alcohol, spicy foods, and artificial sweeteners.
2- Medications
- Antispasmodic Medications: These medications help relieve abdominal cramping and pain by relaxing the muscles of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Laxatives or Anti-Diarrheal Medications: Depending on your predominant symptoms (constipation or diarrhea), your healthcare provider may recommend medications to help regulate bowel movements.
- Probiotics: Some individuals experience symptom relief with certain probiotic supplements, which can help balance gut bacteria.
3- Stress Management
- Relaxation Techniques: Stress and anxiety can exacerbate IBS symptoms. Practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can help manage stress.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a therapeutic approach that can help individuals with IBS address the psychological factors that may contribute to their symptoms.
4. Regular Exercise
Regular physical activity can help regulate bowel movements, reduce stress, and improve overall well-being. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
5. Medication for Specific Symptoms
If your IBS symptoms are severe or significantly impact your daily life, your healthcare provider may prescribe medications that target specific symptoms, such as diarrhea, constipation, or abdominal pain.
6. Mindful Eating
Practising mindful eating involves paying close attention to your food, savoring each bite, and eating slowly. This approach can help you become more attuned to your body’s signals and reduce overeating or consuming trigger foods.
7. Keep a Symptom Journal
Keeping a detailed journal of your diet, symptoms, and daily activities can help identify patterns and triggers. This information can be invaluable when working with healthcare providers to develop a personalized management plan.
8. Support Groups
Joining an IBS support group or seeking therapy can provide emotional support and coping strategies for dealing with the challenges of living with a chronic condition.
Conclusion
While Irritable Bowel Syndrome can be frustrating and disruptive, it is a manageable condition. Effective management often involves a combination of dietary modifications, medications, stress management techniques, and lifestyle adjustments. It’s important to work closely with healthcare providers, including gastroenterologists and dietitians, to create a personalized treatment plan that addresses your specific symptoms and needs. By taking proactive steps and making informed choices, individuals with IBS can improve their quality of life and minimize the impact of this condition on their daily activities.