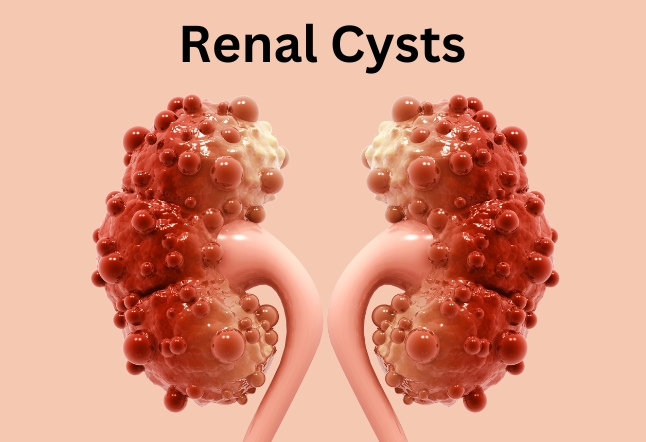
What Are Simple Kidney Cysts?
Simple kidney cysts, also known as renal cysts, are small, round sacs filled with clear fluid that develop within the kidneys. These cysts are typically noncancerous (benign) and do not interfere with kidney function. Simple kidney cysts are distinct from polycystic kidney disease (PKD), a genetic condition characterized by the growth of numerous cysts in the kidneys, which can lead to kidney damage.
Causes of Simple Kidney Cysts
The exact cause of simple kidney cysts is not well understood. However, several factors may contribute to their development:
- Aging: Simple kidney cysts are more common in individuals over the age of 50, suggesting a possible age-related component.
- Genetics: There may be a genetic predisposition to developing kidney cysts, as they can run in families.
- Obstruction of Tubules: Some theories suggest that the obstruction of small tubules within the kidney may lead to the formation of cysts.
Symptoms of Simple Kidney Cysts
In many cases, simple kidney cysts do not cause any noticeable symptoms and are often discovered incidentally during imaging tests for unrelated health issues. However, when symptoms do occur, they may include:
- Dull Flank Pain: Some individuals with kidney cysts may experience a dull, aching pain in the side or back, where the kidneys are located.
- Abdominal Discomfort: Cysts that become enlarged can cause a feeling of fullness or discomfort in the abdomen.
- Hematuria: In rare cases, kidney cysts may lead to blood in the urine (hematuria).
Diagnosis of Simple Kidney Cysts
Diagnosing simple kidney cysts typically involves a combination of the following:


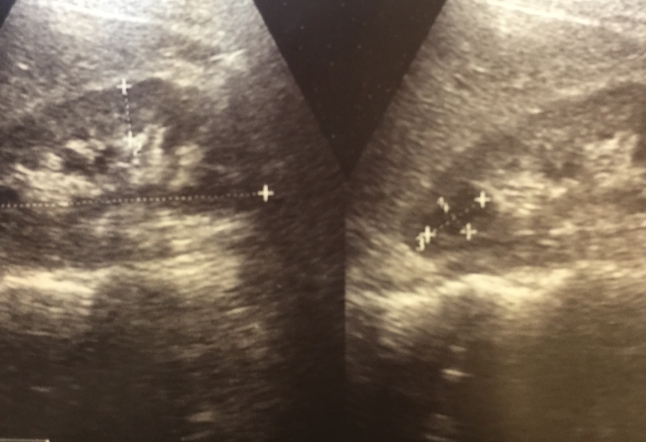
- Imaging Tests: The most common method of diagnosis is through imaging studies such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI scans, which can visualize the cysts and their characteristics.
- Clinical Evaluation: A healthcare provider will take a detailed medical history and perform a physical examination to assess symptoms and overall health.
Kidney Cyst Treatment and management
Treatment and management of simple kidney cysts typically depend on the size of the cyst, the presence of symptoms, and the potential for complications. Many simple kidney cysts are small and asymptomatic, requiring no intervention. However, if cysts are causing discomfort or complications, several approaches can be considered:
Observation and Monitoring
If the kidney cysts are small (typically less than 4 cm or 1.6 inches in diameter) and not causing symptoms, your healthcare provider may recommend a watchful waiting approach. Regular follow-up with imaging tests, such as ultrasound or CT scans, can help monitor cyst growth and any associated symptoms.

Pain Management
Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen (Tylenol) or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) may be recommended to manage mild pain or discomfort associated with kidney cysts.
Cyst Aspiration
If a cyst is large and causing significant pain or discomfort, or if there is uncertainty about its nature, cyst aspiration may be performed. This is a minimally invasive procedure in which a thin needle is inserted into the cyst to drain the fluid. Aspiration can provide temporary relief from symptoms.
Sclerotherapy
Sclerotherapy is a procedure that may be used in combination with cyst aspiration. After draining the cyst, a sclerosing agent (such as alcohol or saline) is injected into the cyst cavity to prevent it from refilling with fluid. This can be effective in reducing the recurrence of the cyst.
Surgical Intervention
Surgical removal of a kidney cyst is rarely necessary and is usually reserved for large cysts causing severe symptoms, complications (such as infection or bleeding), or when there is uncertainty about the cyst’s nature.
Partial or complete nephrectomy (removal of part or all of the kidney) may be considered if the cyst is part of a larger kidney issue or if there is a suspicion of malignancy (although simple kidney cysts are typically not cancerous).
Lifestyle and Dietary Modifications
While not a direct treatment for kidney cysts, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help manage overall kidney health. This includes staying well-hydrated, following a balanced diet, and managing conditions like hypertension that can affect kidney function.
Regular Follow-Up
If you have simple kidney cysts, it’s essential to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for monitoring and management. Regular check-ups and imaging tests can help detect any changes in cyst size or the development of symptoms.
It’s crucial to note that most simple kidney cysts are benign and do not require aggressive treatment. However, the management approach should be individualized based on the patient’s specific condition and symptoms. Always consult with a healthcare provider for a proper evaluation and personalized treatment plan. Additionally, any sudden or severe symptoms, such as severe pain or signs of infection, should prompt immediate medical attention.